Spring (VS) Springboot
Spring is a popular framework for creating scalable web applications, with Spring MVC being a widely used module for building such applications. However, traditional Spring projects can be time-consuming and complex to configure, especially for new developers, making production readiness a challenge.
Spring Boot addresses this issue by building on top of Spring, offering a rapid, production-ready environment. It simplifies configuration, allowing developers to focus on business logic rather than setup. As a microservice-based framework, Spring Boot enables the quick development of production-ready applications. Basic knowledge of the Spring framework is recommended before diving into Spring Boot.
Why misconfigurations in Spring Boot are a critical security concern?
Misconfigurations in Spring Boot applications pose a significant security concern due to the framework's integration with a wide variety of components and its ability to rapidly develop web applications. Spring Boot has become one of the most popular frameworks for building modern Java applications due to its simplicity, flexibility, and extensive feature set. However, the same flexibility and ease of use that make Spring Boot attractive can also lead to significant security risks when applications are misconfigured.
Spring Boot's flexibility often leads to default configurations being left unchanged. Attackers can exploit these defaults if they are insecure.
For instance:
Default credentials for databases or admin consoles.
Enabled endpoints, such as /actuator, without proper security measures.Common misconfigurations and their risks.
Exposed Actuator endpoints
What is Actuator ?? Developing and Managing an application are the two most important aspects of the application’s life cycle.Monitoring the application during both development and production is essential for understanding its internal workings and ensuring smooth operations.
Spring Boot simplifies monitoring and management with its Actuator dependency. By leveraging endpoints like /actuator and /actuator/health, developers can monitor application health and performance effectively using HTTP-based tools. This makes actuator a valuable resource for maintaining Spring Boot applications.
Actuator configuration in pom.xml for maven
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>How to enable actuator endpoint?
Add the management.endpoints.web.base-path in application.properties
spring.application.name=blog
server.port=1337
management.endpoints.web.base-path=/actuatorThe path would be http://localhost:1337/actuator.
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:1337/actuator",
"templated": false
},
"health": {
"href": "http://localhost:1337/actuator/health",
"templated": false
},
"health-path": {
"href": "http://localhost:1337/actuator/health/{*path}",
"templated": true
}
}
}The response should be like the above.
So , what if the developer had a configuration like this in application.properties
spring.application.name=blog
server.port=1337
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
management.endpoints.web.base-path=/actuator
management.endpoint.env.show-details=always- Application Name: Sets the app's name to
blog(spring.application.name). - Server Port: Runs the app on port
1337(server.port). - Actuator Endpoints: Exposes all Actuator endpoints (
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*) under the base path/actuator(management.endpoints.web.base-path). - Environment Details: Configures the
/actuator/envendpoint to always show detailed environment information (management.endpoint.env.show-details=always).
How to exploit this and leak sensitive data's
Exposed /heapdump endpoint
The /heapdump endpoint provides a snapshot of the Java heap, which includes memory allocation details.
We can download the heapdump file by acessing this http://localhost:1337/actuator/heapdump endpoint.
Analysing the heapdump
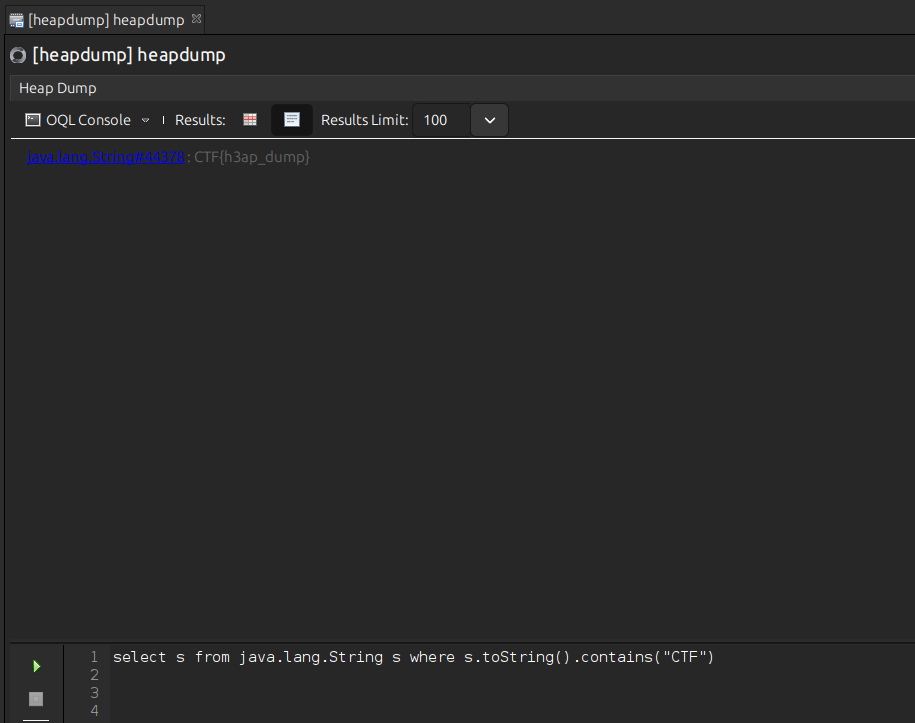
file heapdump
heapdump: Java HPROF dump, created Thu Dec 19 11:15:39 2024We need to analyse this heapdump via VisualVM (opens in a new tab) and extract sensitive information.
Open the heapdump file in VisulaVM and navigate to the Heap Dump tab to inspect memory objects.Open the OQL(object query language) console and execute queries to search for sensitive information.
For strings containing token or key:
select s from java.lang.String s where s.toString().contains("token")For environment like variables:
select s from java.lang.String s where s.toString().contains("apiKey")Results may reveal access tokens, API keys or credentials stored in memory.
Exposed /mappings endpoint
The /mappings endpoint provides information about the application’s request mappings.
We can access this via http://localhost:1337/actuator/mappings.
{
"predicate": "{GET [/internal-endpoint-leak]}",
"handler": "com.blogs.blog.controller.BlogController#internal()",
"details": {
"handlerMethod": {
"className": "com.blogs.blog.controller.BlogController",
"name": "internal",
"descriptor": "()Ljava/lang/String;"
},
"requestMappingConditions": {
"consumes": [],
"headers": [],
"methods": [
"GET"
],
"params": [],
"patterns": [
"/internal-endpoint-leak"
],
"produces": []
}
}
},
{
"predicate": "{GET [/flag]}",
"handler": "com.blogs.blog.controller.BlogController#secret()",
"details": {
"handlerMethod": {
"className": "com.blogs.blog.controller.BlogController",
"name": "secret",
"descriptor": "()Ljava/lang/String;"
},
"requestMappingConditions": {
"consumes": [],
"headers": [],
"methods": [
"GET"
],
"params": [],
"patterns": [
"/flag"
],
"produces": []
}
}
},It discloses debug routes,hidden endpoints not meant for public use.
Exposed /beans endpoint
The /actuator/beans endpoint in a Spring Boot application provides a list of all the Spring beans that are defined in the application context. This can include components like services, controllers, repositories, and other beans managed by the Spring container.
The response for /actuator/beans endpoint might look like this:
},
"org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration$ThymeleafWebMvcConfiguration$ThymeleafViewResolverConfiguration": {
"aliases": [],
"scope": "singleton",
"type": "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration$ThymeleafWebMvcConfiguration$ThymeleafViewResolverConfiguration",
"dependencies": []
},
"userService": {
"aliases": [],
"scope": "singleton",
"type": "com.blogs.blog.BlogService.UserService",
"resource": "file [/home/leodass/Downloads/blog/target/classes/com/blogs/blog/BlogService/UserService.class]",
"dependencies": []
},
"org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.endpoint.web.servlet.WebMvcEndpointManagementContextConfiguration": {
"aliases": [],
"scope": "singleton",
"type": "org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.endpoint.web.servlet.WebMvcEndpointManagementContextConfiguration",
"dependencies": []
},
"viewResolver": {
"aliases": [],
"scope": "singleton",
"type": "org.springframework.web.servlet.view.ContentNegotiatingViewResolver",
"resource": "class path resource [org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/web/servlet/WebMvcAutoConfiguration$WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter.class]",
"dependencies": [
"org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration$WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter",
"org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@67545b57"
]
},The beans that are exposed could include sensitive application components like services handling authentication, authorization, encryption, etc.The list of beans reveals the internal architecture of the application, including how components interact with each other. This can help attackers identify weak points or areas where they can perform targeted attacks.
Exposed /metrics endpoint
Spring Boot Actuator Metrics provides built-in, production-ready features to help monitor and manage a Spring Boot application. It exposes various metrics that give insights into the health, performance, and operational state of the application. These metrics include information about system resources, application health, application performance, and the behavior of application components.
{
"names": [
"application.ready.time",
"application.started.time",
"disk.free",
"disk.total",
"executor.active",
"executor.completed",
"executor.pool.core",
"executor.pool.max",
"executor.pool.size",
"executor.queue.remaining",
"executor.queued",
"http.server.requests",
"http.server.requests.active",
"jvm.buffer.count",
"jvm.buffer.memory.used",
"jvm.buffer.total.capacity",
"jvm.classes.loaded",
"jvm.classes.unloaded",
"jvm.compilation.time",
"jvm.gc.live.data.size",
"jvm.gc.max.data.size",
"jvm.gc.memory.allocated",
"jvm.gc.memory.promoted",
"jvm.gc.overhead",
"jvm.gc.pause",
"jvm.info",
"jvm.memory.committed",
"jvm.memory.max",
"jvm.memory.usage.after.gc",
"jvm.memory.used",
"jvm.threads.daemon",
"jvm.threads.live",
"jvm.threads.peak",
"jvm.threads.started",
"jvm.threads.states",
"logback.events",
"process.cpu.time",
"process.cpu.usage",
"process.files.max",
"process.files.open",
"process.start.time",
"process.uptime",
"system.cpu.count",
"system.cpu.usage",
"system.load.average.1m",
"tomcat.sessions.active.current",
"tomcat.sessions.active.max",
"tomcat.sessions.alive.max",
"tomcat.sessions.created",
"tomcat.sessions.expired",
"tomcat.sessions.rejected"
]
}The exposure of sensitive details through /actuator/metrics/{exposed-endpoint}, including internal IP addresses, session endpoints, and request patterns, can pose a security risk. This information could be exploited by attackers to map the application and plan targeted attacks.
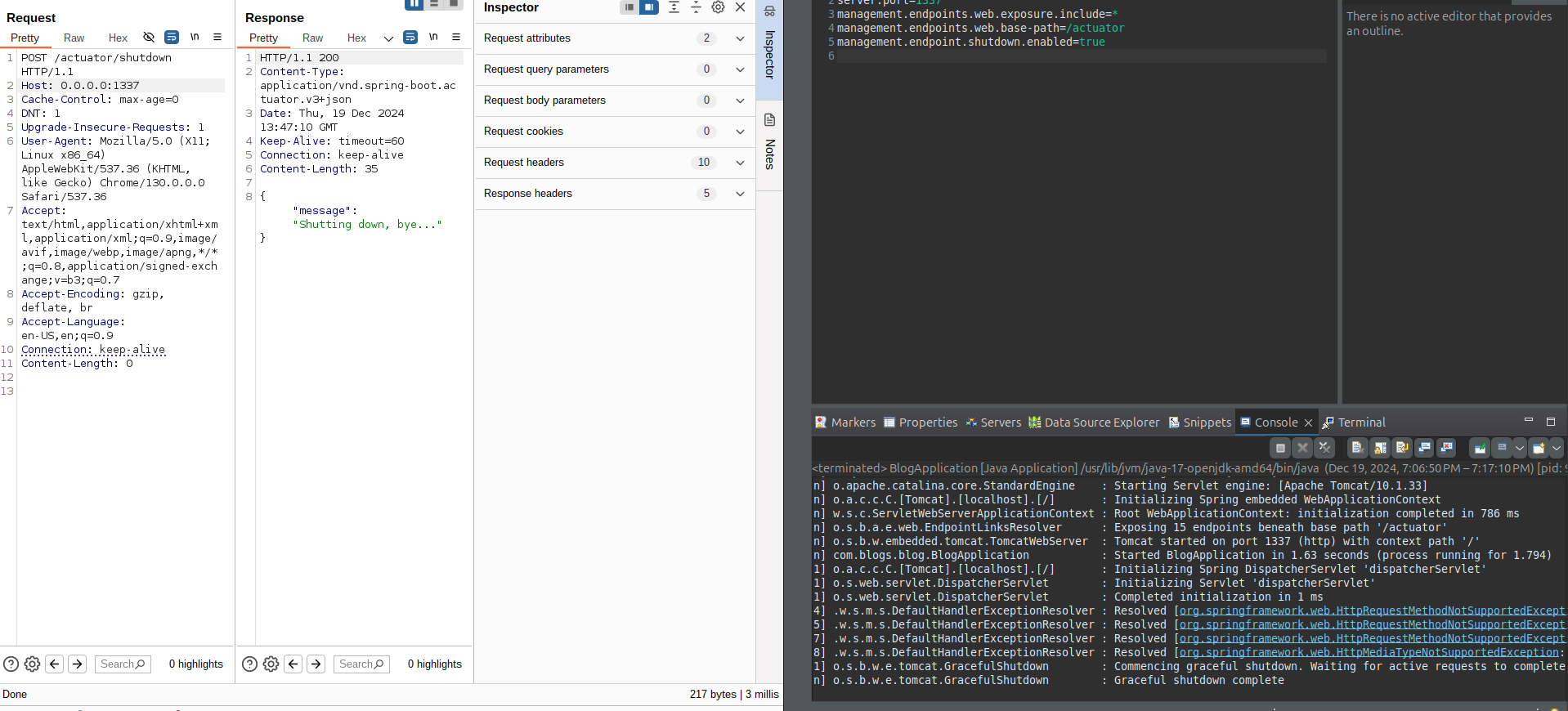
Exposed /shutdown endpoint
The shutdown endpoint is used to shut down the application.
To shut down the application, make a POST request to /actuator/shutdown
Spring Expression Language (SpEL) injection
Spring Expression Language (SpEL) (opens in a new tab) is a powerful expression language used within the Spring Framework for querying and manipulating object graphs at runtime. It provides the ability to access and manipulate objects in a Spring application.
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'I am Leo'.concat('DASS')");
String message = exp.getValue(exp,String.class);
System.out.println(message);An instance of SpelExpressionParser is used to parse SpEL expressions.The expression 'I am Leo'.concat('DASS') appends 'DASS' to 'I am Leo' using the concat method.The getValue() method evaluates the parsed expression and returns the result as a String.The resulting string "I am LeoDASS" is printed.
SpEL allows dynamic runtime evaluation of Java-like expressions, enabling flexibility in configurations and logic.
In Spring Expression Language (SpEL), EvaluationContext plays a key role in evaluating expressions. The two commonly used contexts are StandardEvaluationContext and SimpleEvaluationContext.
StandardEvaluationContext:
The StandardEvaluationContext in Spring Expression Language (SpEL) is a powerful and versatile context designed for evaluating complex expressions. It provides a rich set of features, enabling SpEL expressions to interact with the application’s data, methods, and logic dynamically.
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setVariable("user", "Leodass");
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello, '.concat(#user)");
String message = exp.getValue(context, String.class);
System.out.println(message);Output
Hello, LeodassYou can define variables within the context and use them dynamically in expressions.Variables are referenced using the # symbol in SpEL.
Method Invocation
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'leodass'.toUpperCase()");
String result = exp.getValue(context, String.class);
System.out.println(result);Allows calling methods of objects directly within expressions.
public class ParseService {
public final SensitiveService sensitiveService = new SensitiveService();
public void parseUserInput(String userInput) {
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(this);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression(userInput);
String result = exp.getValue(context, String.class);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ParseService service = new ParseService();
service.parseUserInput("{user_input}");
}
}Can you able to find the vulnerability here??
Since sensitiveService is public, SpEL can directly access it without further configuration.if the sensitiveService has any sensitive methods , we can able to invoke those methods by exploiting this.
With great power comes great responsibility. Since
StandardEvaluationContextprovides access to methods, types, and more, it can pose a security risk if user-controlled input is evaluated. Always validate and sanitize inputs to prevent malicious code execution.
SimpleEvaluationContext
A lightweight and restricted context primarily for use cases with minimal security risks and limited capabilities.Access and modify public properties or fields.Does not allow method calls, type access, or advanced operations like defining variables.
Usage: Ideal for scenarios with simpler needs or when you want to restrict what SpEL expressions can do for security reasons.
SimpleEvaluationContext SimpleContext = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();
StandardEvaluationContext StandardContext = new StandardEvaluationContext();
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('id')");
Object standardmessage = exp.getValue(StandardContext);
System.out.println("Standard : "+standardmessage);
Object simplemessage = exp.getValue(SimpleContext);
System.out.println("Simple : "+simplemessage);Output
Standard : Process[pid=1006688, exitValue=0]
2024-12-20T12:08:52.915+05:30 ERROR 1006622 --- [blog] [nio-1337-exec-1] o.a.c.c.C.[.[.[/].[dispatcherServlet] : Servlet.service() for servlet [dispatcherServlet] in context with path [] threw exception [Request processing failed: org.springframework.expression.spel.SpelEvaluationException: EL1005E: Type cannot be found 'java.lang.Runtime'] with root causeMisconfigured CORS policies
A misconfigured CORS (opens in a new tab) policy can lead to severe security vulnerabilities, such as exposing sensitive data or enabling cross-origin attacks.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class TestController {
@CrossOrigin(origins = "*")
@GetMapping("/data")
public String corstest() {
return "internal data";
}
}In the given Spring Boot code, the TestController class is a REST controller that handles HTTP requests at the /api endpoint. The @RequestMapping("/api") annotation maps the controller to the /api base path. Inside this controller, there is a method corstest() annotated with @CrossOrigin(origins = "*"), which means that it allows cross-origin requests from any origin, effectively making the /api/data endpoint accessible to any external domain. This is particularly useful in scenarios where the backend needs to handle requests from different domains. The @GetMapping("/data") annotation specifies that the corstest() method should handle GET requests made to the /api/data URL, and it simply returns a string message "internal data". The @CrossOrigin annotation in this case can be considered a security risk as it opens up the endpoint to be accessed from any domain, which can expose the application to potential cross-site scripting (XSS) and other security vulnerabilities if not managed properly.
By default, Spring does not allow
allowCredentialsto be set totruewhen theoriginis set to*because this combination violates the CORS specification; when enabling credentials, you must explicitly specify allowed origins instead of using the wildcard "*" to ensure security.
So what if developer is come up with this CORS pattern??
@Configuration
public class VulnerableCORSconfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport{
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowedOriginPatterns("https://*.com")
.allowedHeaders("*")
.allowCredentials(true);
}
}Since the allowCredentials(true) configuration is used, this allows cookies and other authentication information to be sent with cross-origin requests. The allowedOriginPatterns("https://*.com") configuration enables all .com domain from the internet to access the API endpoints.
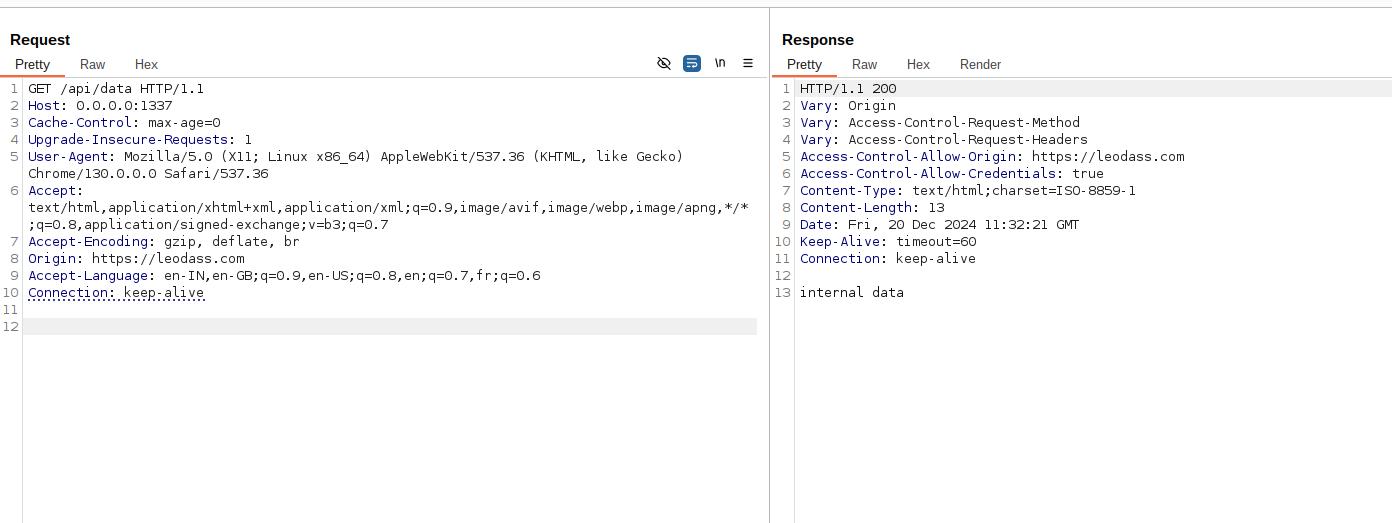
We can host a malicious website on our domain (e.g., attacker.com) and craft a request to the vulnerable API. If the user is logged into the application, their credentials (like session cookies) will be sent along with the request because of the allowCredentials(true) setting. This means we can perform actions on behalf of the logged-in user, potentially leading to unauthorized actions (like changing account settings, making financial transactions, etc.).
Resources
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/reference/actuator/enabling.html (opens in a new tab) https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/3.0.x/reference/expressions.html (opens in a new tab) https://spring.io/guides/gs/rest-service-cors (opens in a new tab)
